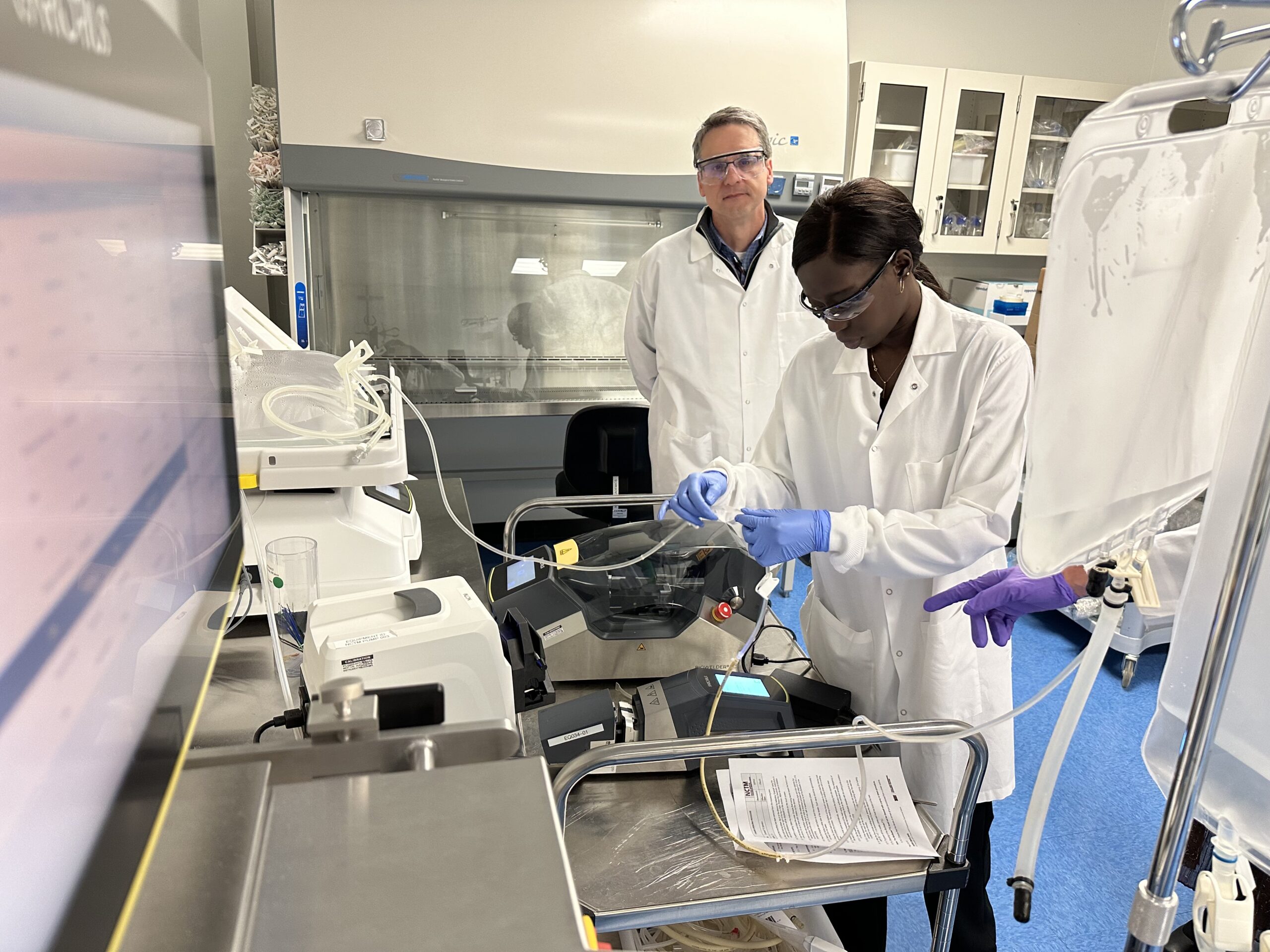
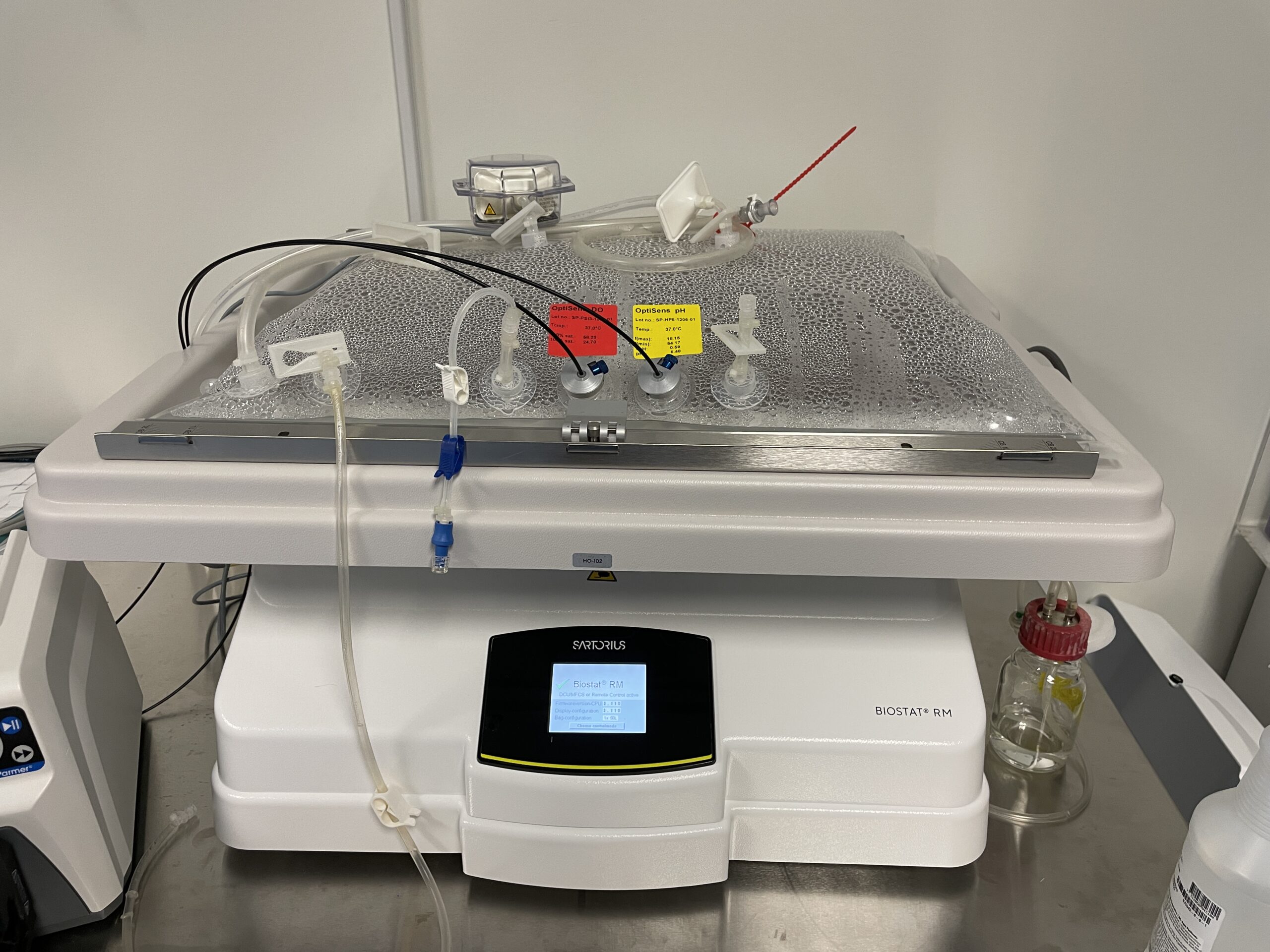
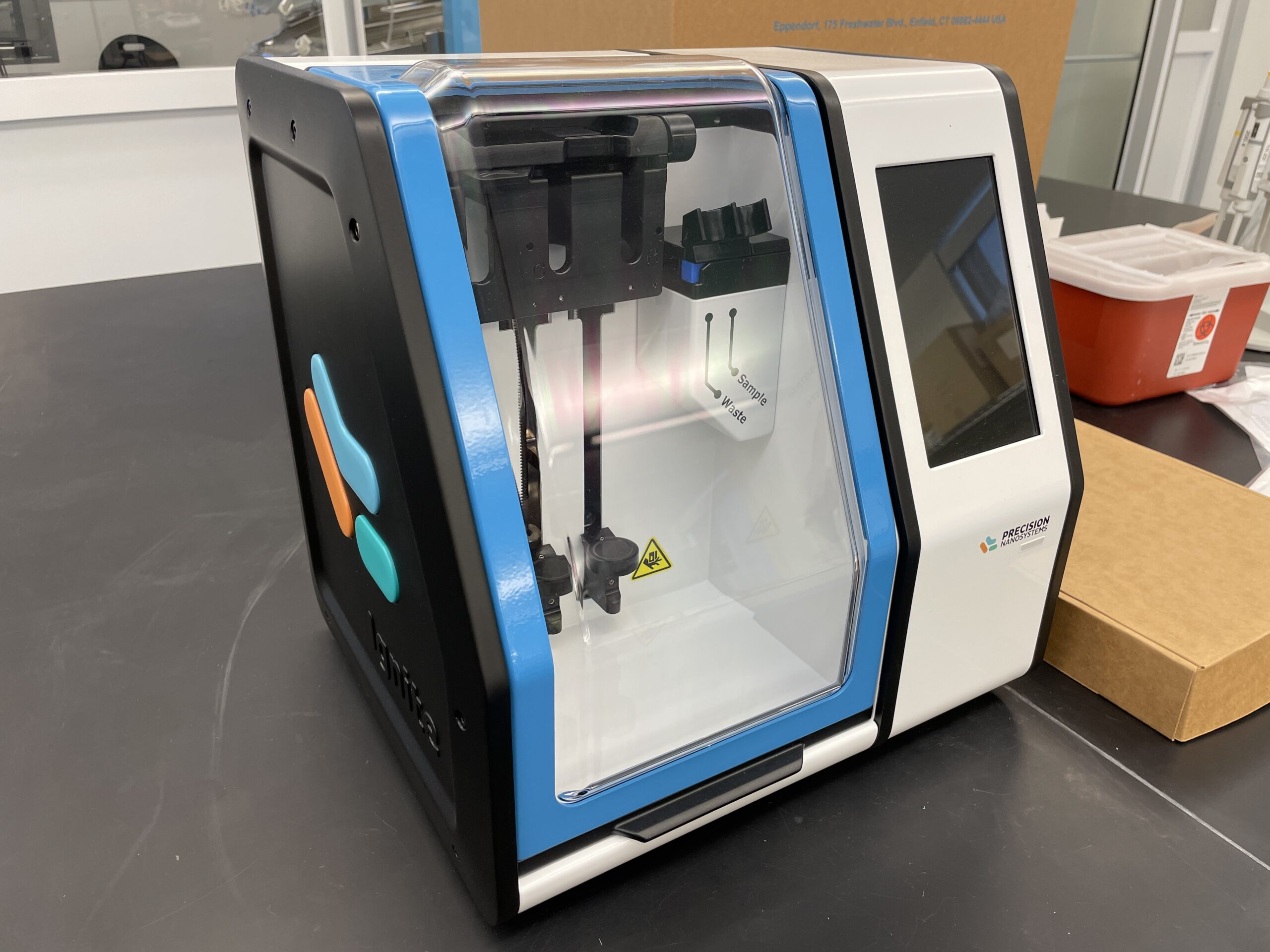
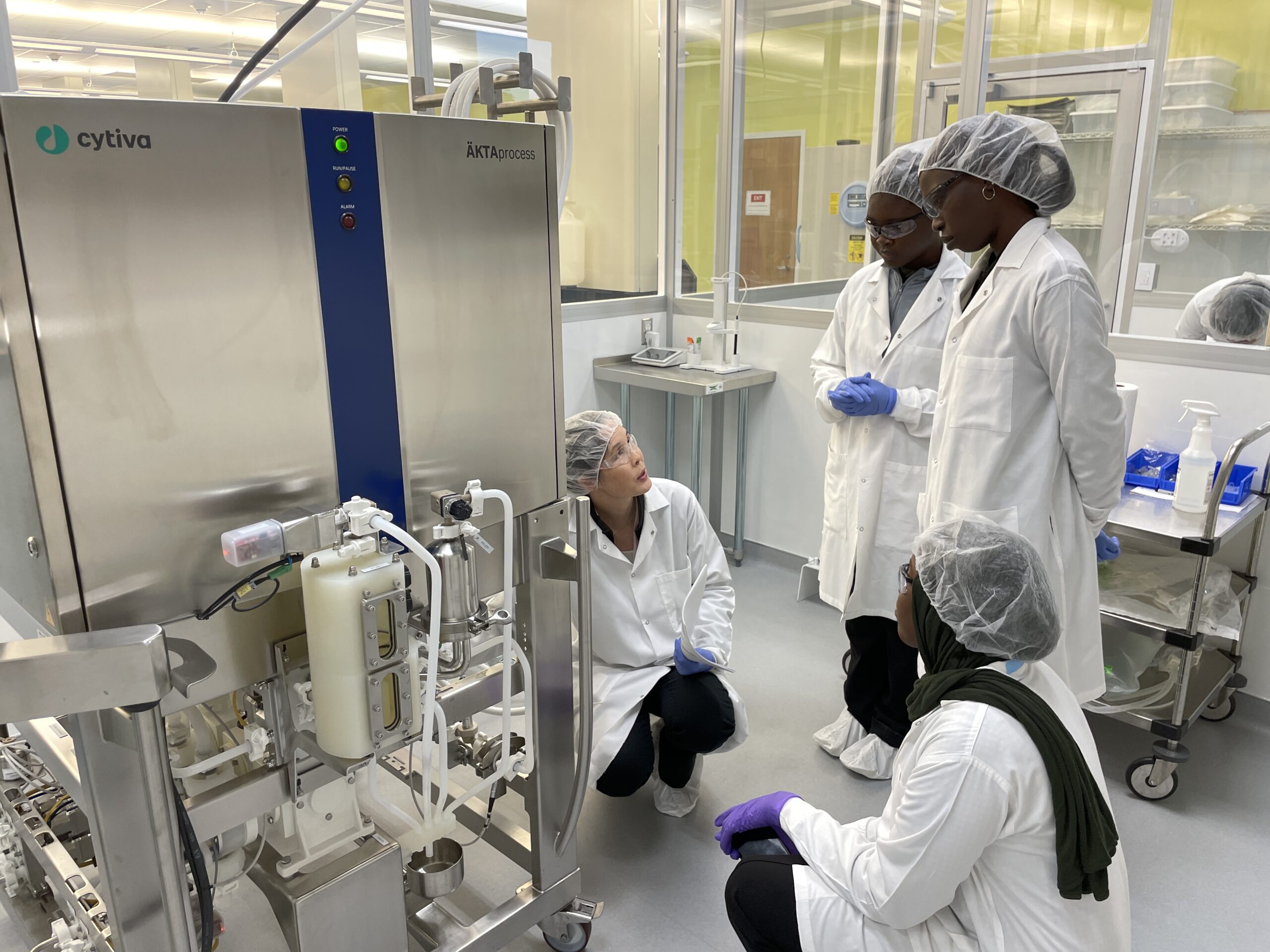
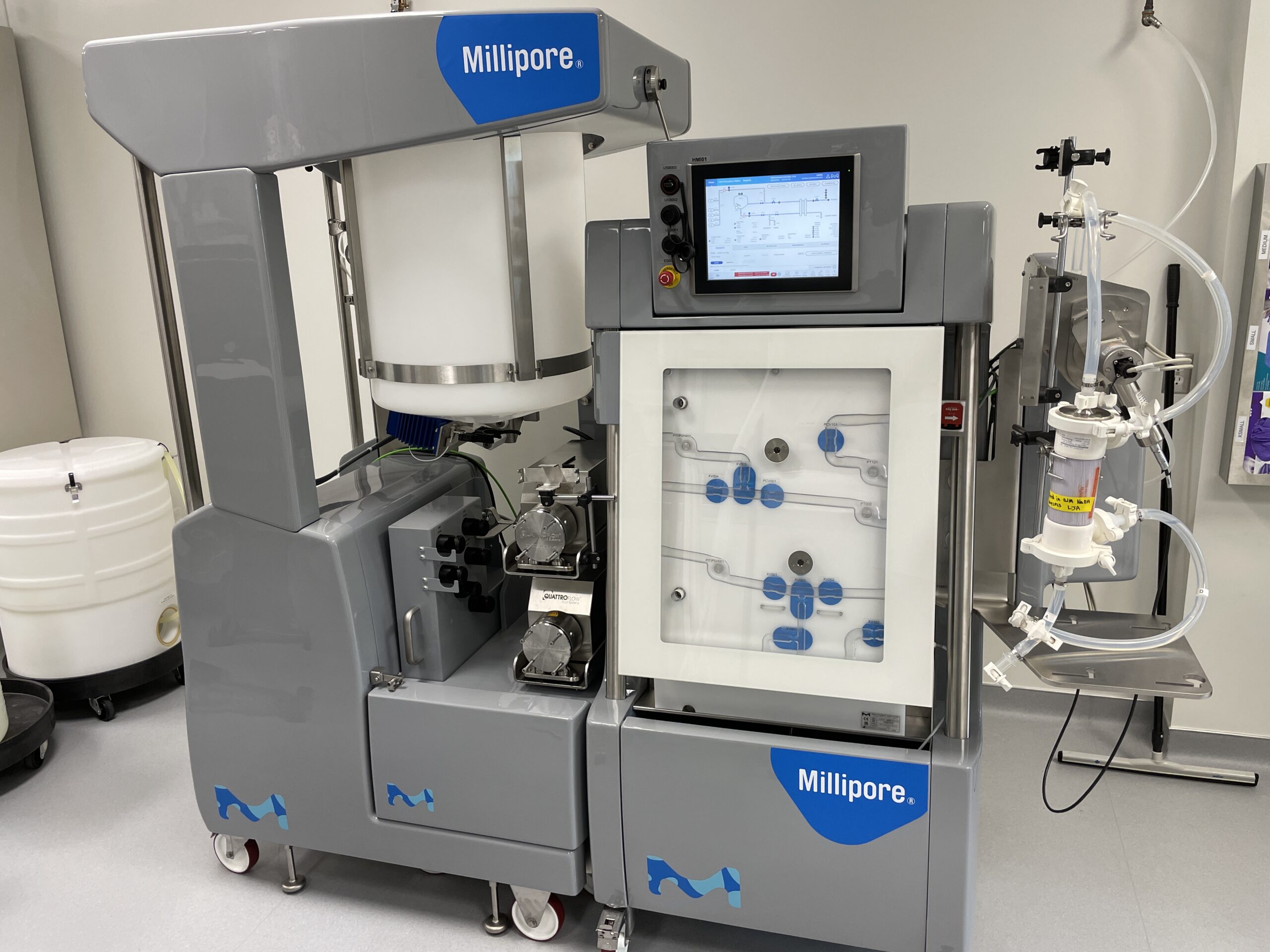
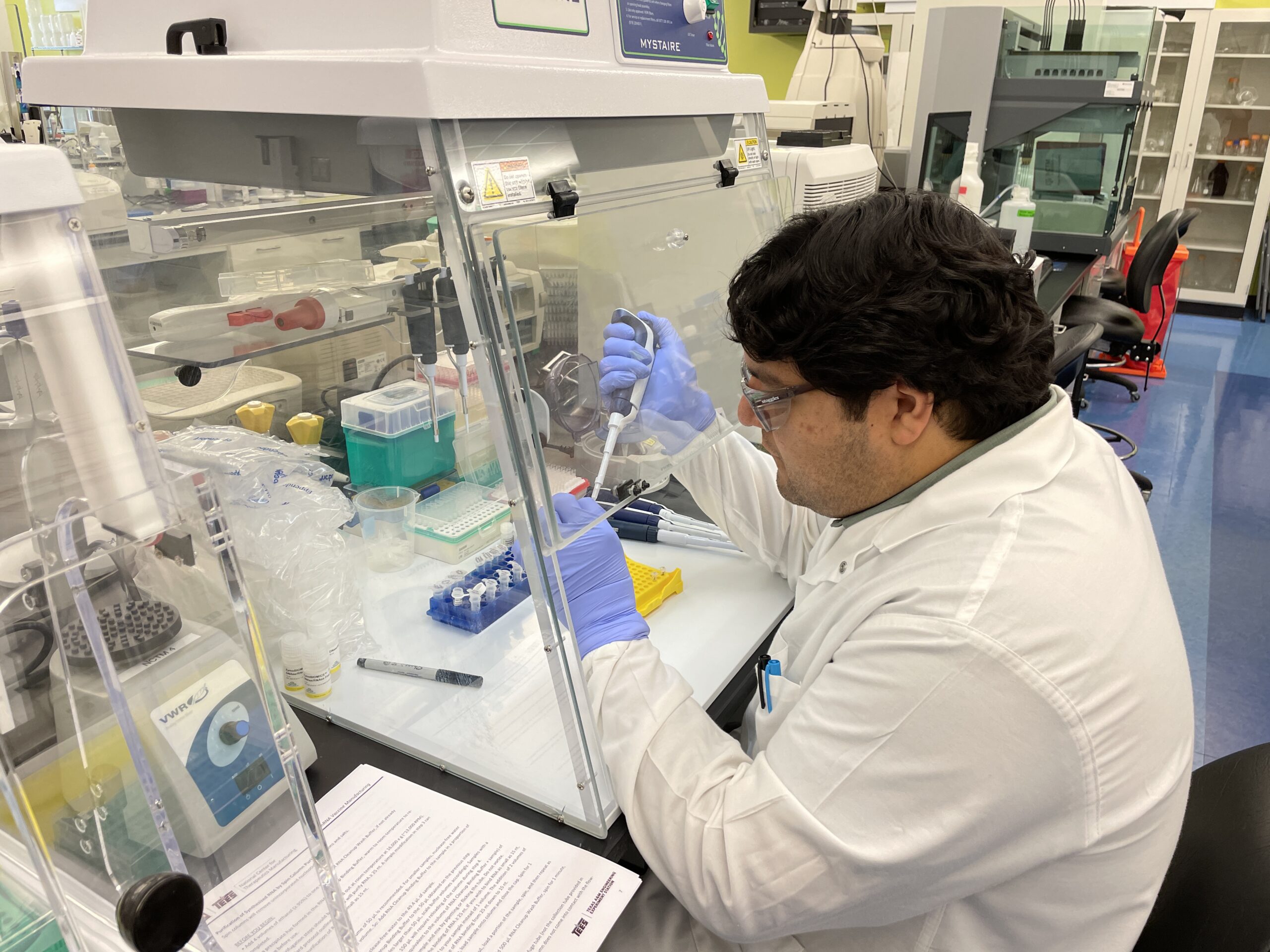
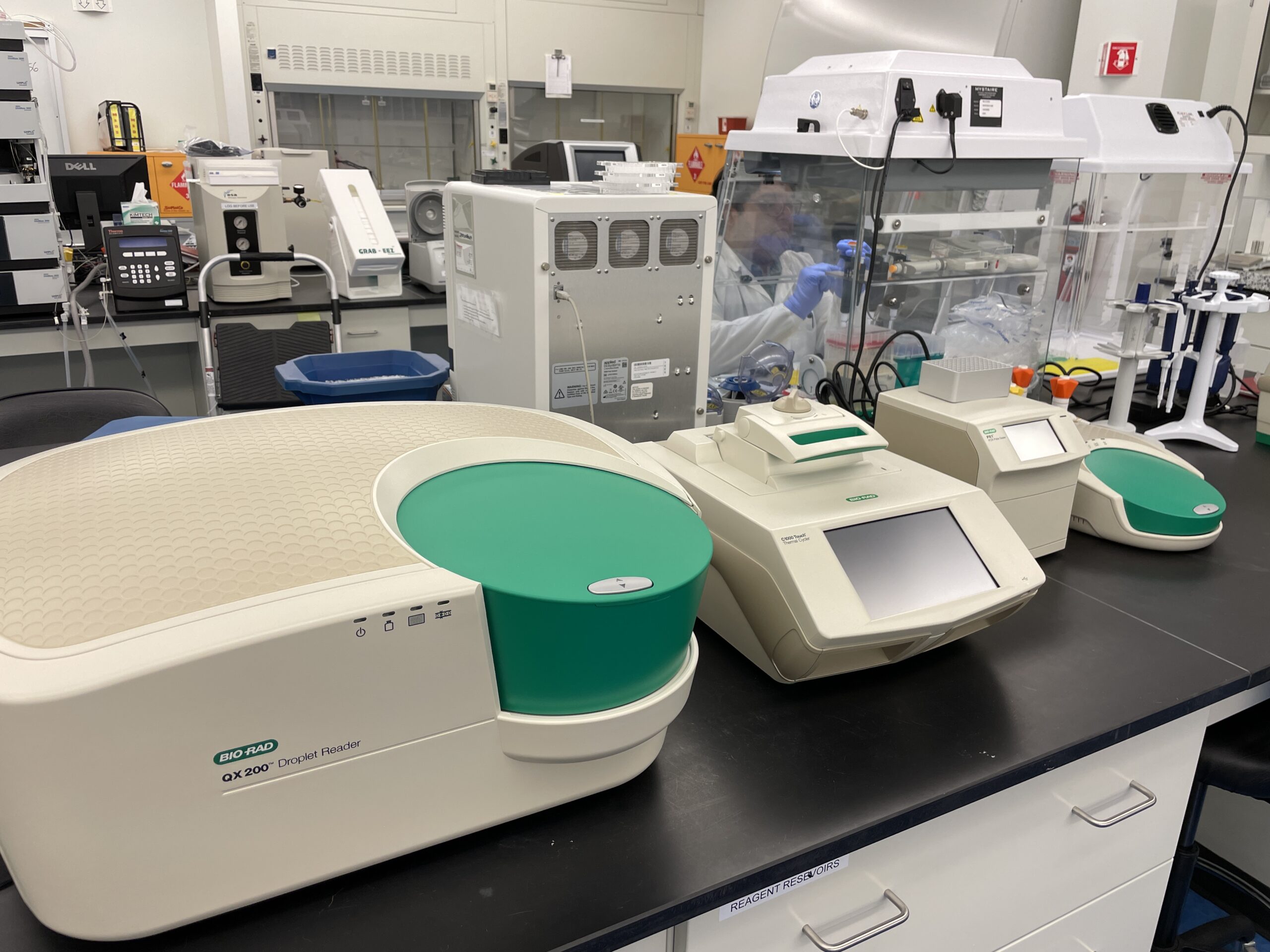
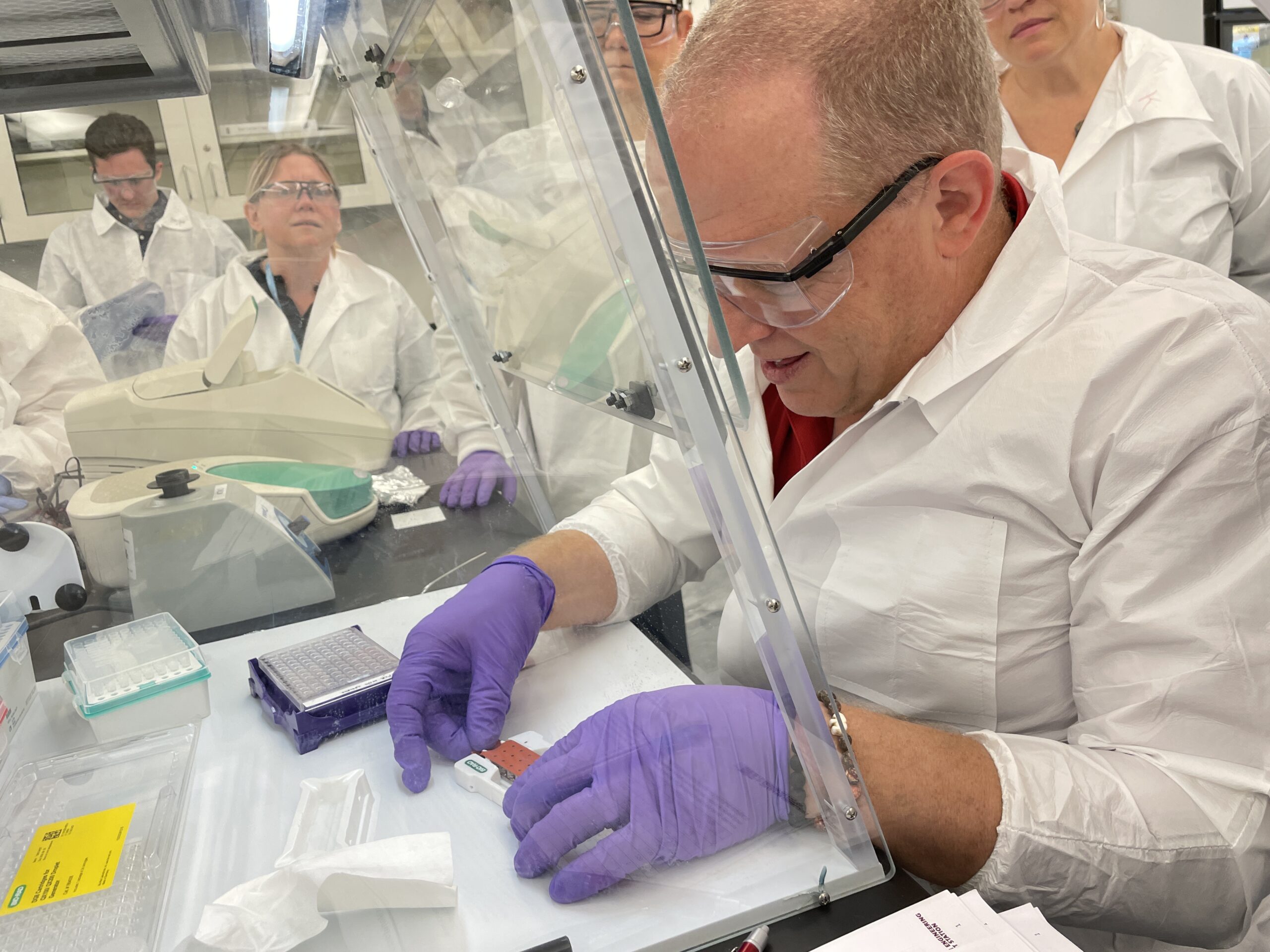
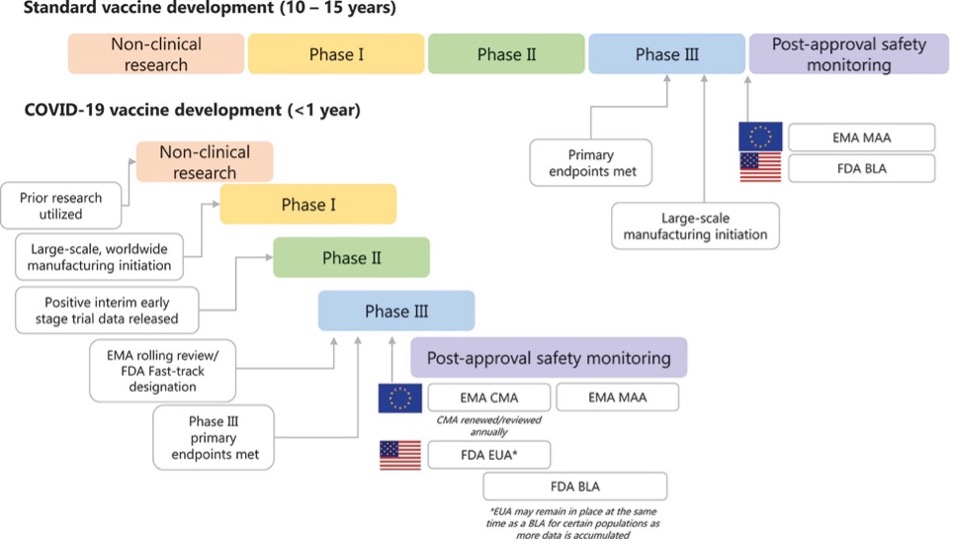
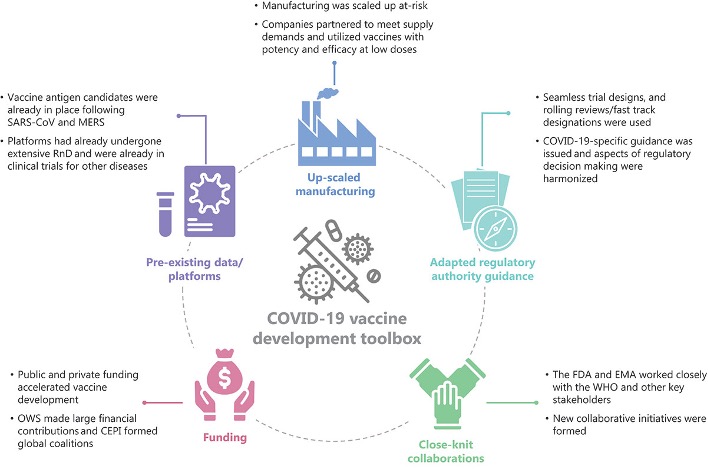
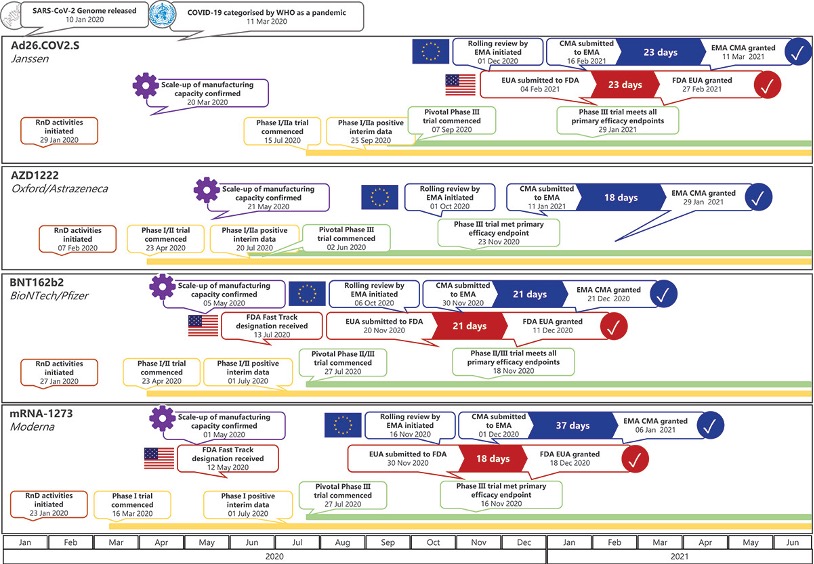
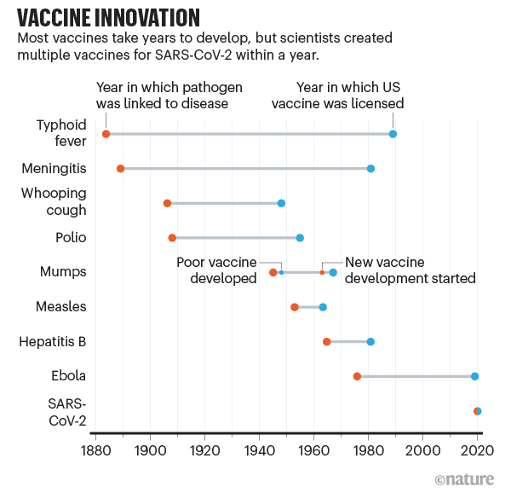
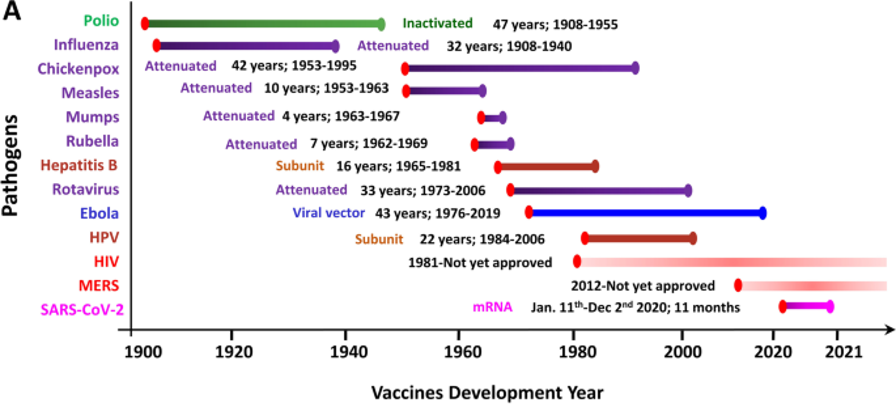
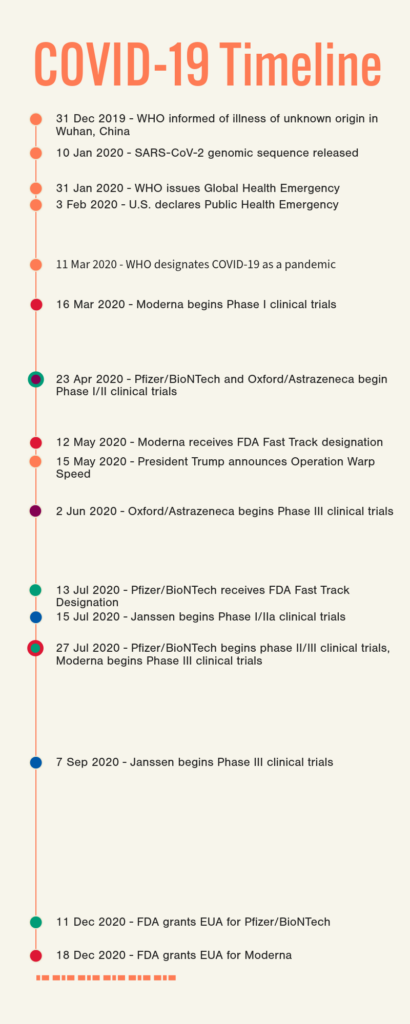
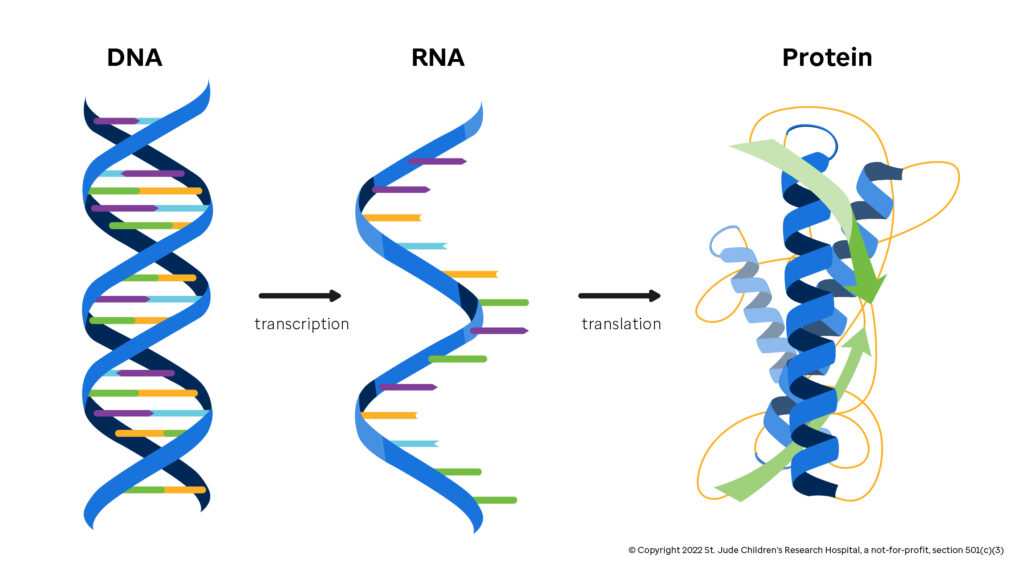
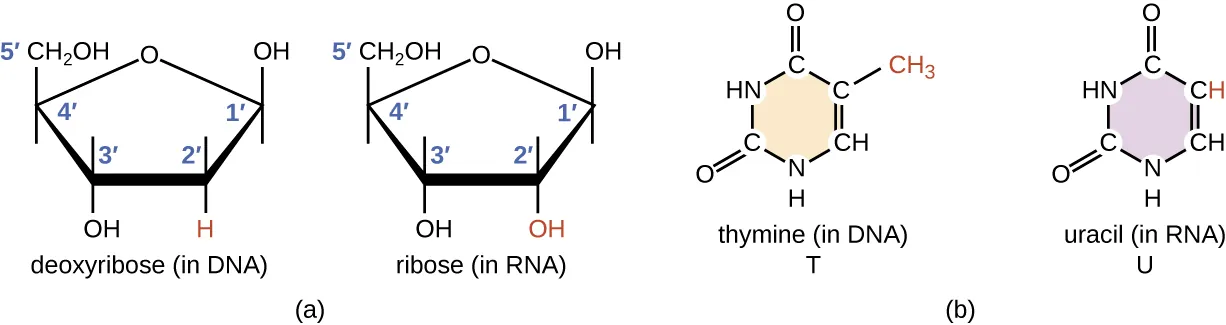
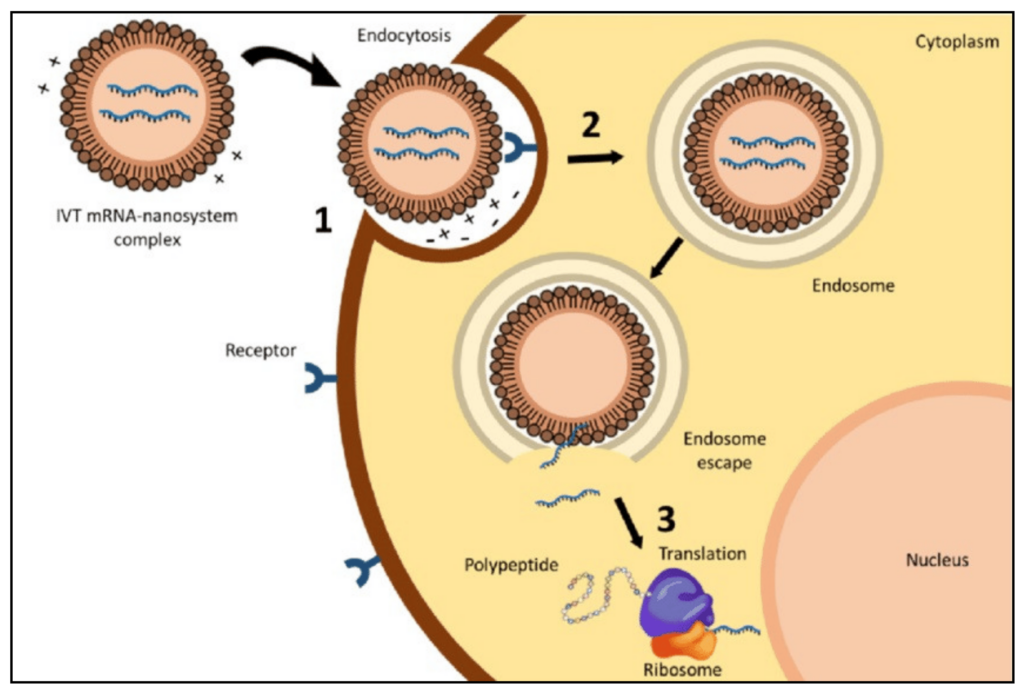
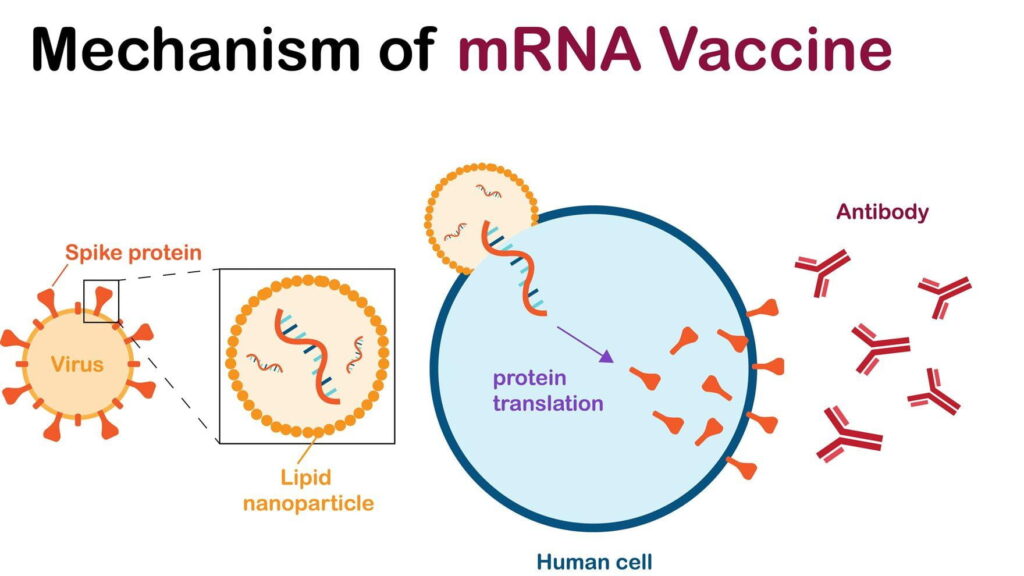
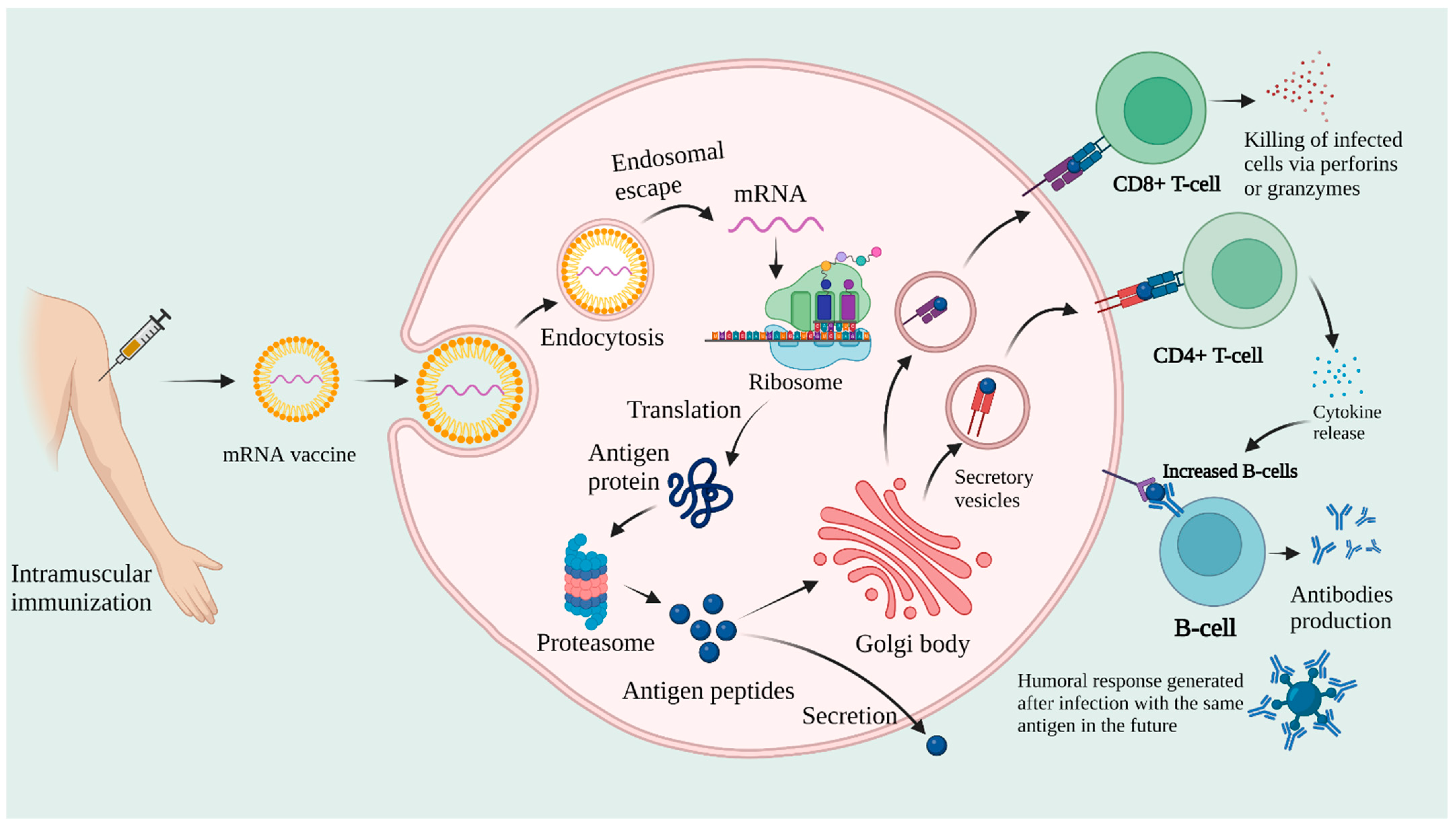
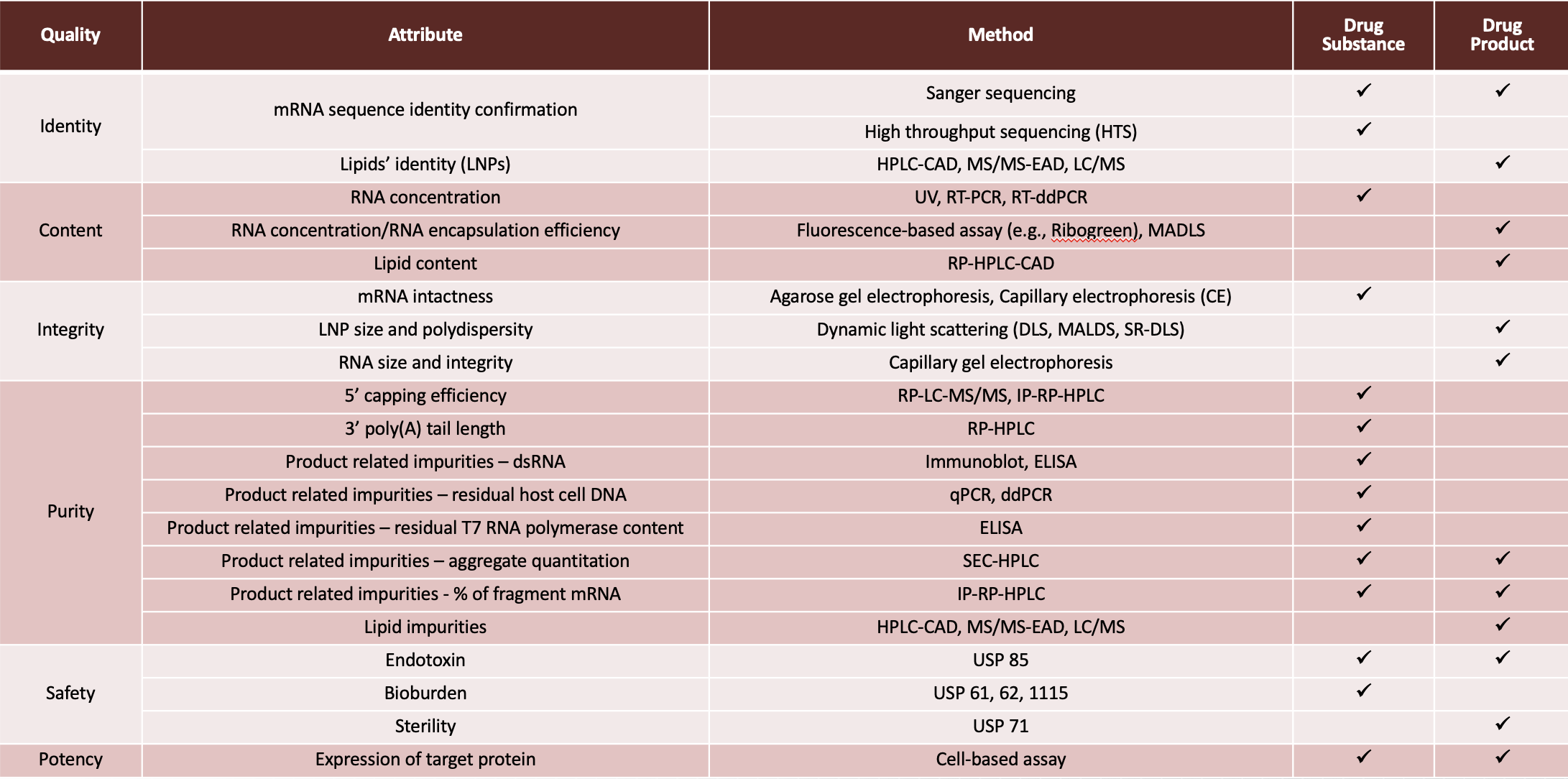
NCTM offers a Hands-on Manufacturing of mRNA Vaccines and Therapeutics training course in our simulated cGMP facility. For more information click below:

Antigen Hero Music Video
For more information regarding customized trainings and the mRNA Vaccine Manufacturing course, please email Programs@NCTMmail.tamu.edu
Ready to enroll? View our calendar to find upcoming mRNA Vaccine Manufacturing trainings.